Page 46 - MC14326 all pages
P. 46
42 | The South African Insurance Industry Survey 2016
Solvency relief and financing transactions contract Of these five, one of the most widely discussed is 80 Collateralized re and others 69
designs may need to be addressed and this technological risk. Examples include autonomous 70 ILW 64
will promote alternative, innovative and tailored vehicles, vulnerability in cloud computing and Sidecar
solutions. cyber security, nanotechnology, infrastructure 8%
breakdown and communications failure. 60 Catastrophe Bonds
Emerging risks 50 28%
Emerging risks are those that are particularly These advancements require insurers to
difficult to identify and predict as these risks determine changes to their insurance products USD billions 50 44 13%
are new and the development of them is largely and offerings. With the introduction of
unknown. The emergence of these risks is autonomous vehicles, this will directly impact the 40
attributed to changes in technology and legal insurance market forcing insurers and reinsurers
theories in our society, which are likely to become to consider the changes that are likely to occur 30 22 24 28 60%
actual claims in the future. In an insurance within the motor insurance space and how to 20 18% 6% 17%
setting, these risks introduce greater uncertainty sustain their business in this new environment. 22
within pricing, reserving, capital modelling and -14%
solvency assessment. However, they may also Implications
present opportunities for innovation and product Emerging risks will force insurers and reinsurers 10
development. to anticipate changes in the insurance market,
particularly in terms of claims, new products and 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 Q3 2015
The more the world is developing and research profitability. Even with the caveats in insurance
is being conducted, the more is discovered policies now, such as restriction to claims-made Source: Aon Benfield
about potential emerging risks particularly for policies, a change in law may expose insurers to
bodily injury and property damage. For example, unexpected risks and potentially large claims, as Reduction in traditional reinsurance capacity and increase in price
research on subatomic particles on the human seen with the asbestos claims. This has a direct following major natural catastrophe events has created the need for
body have shown that everyday products (such as impact on reinsurers particularly for those with no alternative forms of capital. However, the provision of alternative capital
cleaning products) are harming us with the extent aggregated limits. needs to be assessed on both a short- and long-term basis.
of the harm unknown at this point.
Reinsurers have little to no additional information The influx of alternative capital has seen a negative impact on reinsurers
Global emerging risks can be grouped into five to provide technical expertise to insurers on how who have experienced pressure to decrease their reinsurance rates
core categories: to deal with emerging risks and the evolution of particularly in the catastrophe market. However, it is uncertain how
the insurance market. long an increase in alternative capital will last and who will be left to
–– Geopolitical provide capital when the dust settles after a major catastrophe event.
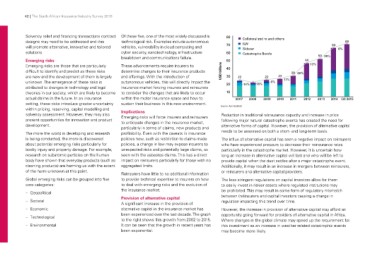
Provision of alternative capital Additionally, it may result in an increase in mergers between reinsurers,
–– Societal A significant increase in the provision of or reinsurers and alternative capital providers.
alternative capital in the insurance market has
–– Economic been experienced over the last decade. The graph The less stringent regulations on capital investors allow for them
to the right shows this growth from 2002 to 2015. to easily invest in riskier assets where regulated institutions may
–– Technological It can be seen that the growth in recent years has be prohibited. This may result in some form of regulatory mismatch
been exponential. between (re)insurers and capital investors causing a change in
–– Environmental regulation impacting this trend over time.
However, the increase in provision of alternative capital may afford an
opportunity going forward for providers of alternative capital in Africa.
Where changes in the global climate may speed up the requirement for
this investment as an increase in weather related catastrophic events
may become more likely.